Bailey's Pocket Mouse
Distribution, Abundance, and Seasonality
In California, occurs in the southeastern corner of the state from Banner (San Diego Co.) on the west of Salton Sea south to the border of Mexico, and along the eastern edge of Imperial Co. at the Colorado River. Locally abundant in California, inhabiting rocky or gravelly slopes with low to moderate shrub cover. Elevational range is 270-720 m (900-2400 ft).
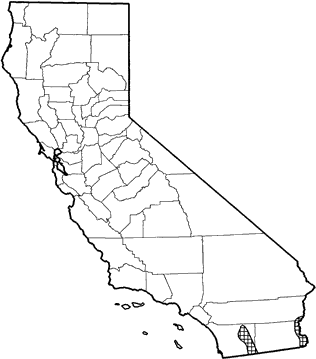
Range Map
Specific Habitat Requirements
Feeding: Forages mainly on seeds of shrubs and forbs (Reichman 1975) but also eats insects and green vegetation seasonally. In Arizona, Bailey's pocket mouse foraged mainly in gravelly soil beneath large desert shrubs (Wondolleck 1978). Seeds are stored in abundance in burrow as well as in other places within the territory.
Cover: Bailey's pocket mouse prefers desert scrub habitat with moderate shrub cover and sandy soils, but can inhabit sparse cover and gravel-pavement substrate.
Reproduction: Burrow excavated at the base of a bush. Underground nest of dried grasses and other plant parts is constructed in burrow.
Water: Water is obtained metabolically from green vegetation and seeds, and from moisture in food.
Pattern: Suitable habitat for Bailey's pocket mouse includes scrub flats or slopes. Agricultural uses preclude its existence. Its occurrence also may be determined by competitive interactions with other pocket mice (C. formosus, C. penicillatus, and C. spinatus).
Species Life History
Activity Patterns: Yearlong activity, although individuals may become torpid over short periods during high summer temperatures. Nocturnal.
Seasonal Movements / Migration: None.
Home Range: Varies from 0.12 to 0.24 ha (0.30 to 0.59 ac), averaging 0.20 ha (0.49 ac) (Reynolds and Haskell 1949, O'Farrell 1978).
Territory: Pocket mice are aggressively solitary. Territory size unknown but probably equal to home range.
Reproduction: Litter size averages 5 young. Gestation is approximately 3-4 wk. Under favorable conditions, young of the year may breed successfully.
Niche: Bailey's pocket mouse is a nocturnal granivore, inhabiting extremely xeric habitats of the Colorado Desert in California. Predators include owls, coyotes, badgers, and snakes. Competitors for food resources include other desert-dwelling rodents (cricetids and heteromyids) and ants.
Sources & References
California Department of Fish and Game, 1999.
California's Wildlife, Sacramento, CA.
Written by: P. Brylski, reviewed by: H. Shellhammer, edited by: R. Duke
O'Farrell, M. J. 1978. Home range dynamics of rodents in a sagebrush community. J. Mammal. 59:657-668. Reichman, O. J. 1975. Relation of desert rodent diets to available resources. J. Mammal. 56:731-751. Reynolds, H. G., and H. S. Haskell. 1949. Life history notes on Price and Bailey pocket mice of southern Arizona. J. Mammal. 30:150-156. Wondolleck, J. T. 1978. Forage-area separation and overlap in heteromyid rodents. J. Mammal. 59:510-518.
California Animal Facts | California's Wildlife