
Cactus Mouse
Distribution, Abundance, and Seasonality
Occurs in southern California, coastally from Ventura Co. south to the border of Mexico, and inland from Death Valley National Monument south throughout the Mojave and Colorado deserts. Elevational range from -75 m (-250 ft) (Grinnell 1937) to 1200 m (4000 ft) (Deacon et al. 1964). Common to abundant in desert riparian, desert scrub, desert wash, Joshua tree, pinyon-juniper, and palm oasis habitats. Common to uncommon in coastal scrub, chamise-redshank and mixed chaparral, and in sagebrush habitats.
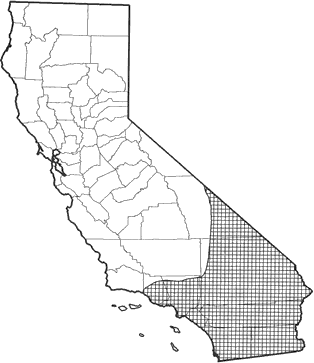
Range Map
Specific Habitat Requirements
Feeding: Feeds on green vegetation, seeds, fruits, and flowers (Bradley and Mauer 1973). Cactus mice in coastal scrub of California feed heavily on shrub foliage, seeds, fruits, and flowers. Insects are moderately important in the diet (Meserve 1976b). Poison-oak is eaten in fall and winter. Treefoil is a major spring food plant, followed by sage and various grasses. In Arizona, arthropods were an important diet element (Reichman and Van de Graaff 1973). Hoards food.
Cover: Generally associated with moderate to dense canopy coverage (Bradley and Mauer 1973, Beatley 1976b, Meserve 1976a).
Reproduction: Little is known about nest characterisics. Probably grass-lined burrows at base of thorny desert shrubs, but also possibly in arboreal nests (McCabe and Blanchard 1950).
Water: Drinks water. Under lab conditions may drink about 11% of body weight (1.8 cc) (0.06 oz) daily (MacMillen 1964). Can survive on only 0.2 cc (0.007 oz) water/day (Lindeborg 1952).
Pattern: Sandy soils are preferred, probably in part for excavating burrows or occupying abandoned burrows.
Species Life History
Activity Patterns: Nocturnal. Active year-round, but shows reduced above-ground activity in hot weather. Can enter torpor when stressed (food deprivation in winter and negative water balance in summer). May be less active on moonlit nights (Owings and Lockard 1971).
Seasonal Movements / Migration: None.
Home Range: Average density in Arizona creosote scrub was 1.09/ha (0.4/ac), ranging from 0.21-3.3/ha (0.09-1.3/ac) (Chew and Chew 1970). In coastal sage scrub, MacMillen (1964) reported densities of 0.2-1.6/ ha (0.08-0.65/ac). Meserve (1977) reported an average home range of 0.42 ha (1.04 ac). Home range in California sage scrub was 0.3 ha (0.75 ac) (MacMillen 1964).
Territory: Aggressively solitary (MacMillen 1964).
Reproduction: Breeds year-round (MacMillen 1964, Rood 1966) over entire range, but in California peaks from April to October (Miller and Stebbins 1964). Gestation period 21-27 days (Svihla 1932). Average litter size varies from 2.5-3.7 (range 1-6, various studies). One to 3 litters per yr (MacMillen 1964). Under lab conditions up to 12 litters per yr, and maximum lifetime litter number of 16. Weaning complete by 25 days (Rood 1966). May breed in first few months.
Niche: Scansorial omnivore with excellent climbing abilities. Potential competitors include Perognathus, over which P. eremicus is said to be behaviorally dominant (MacMillen 1964), and Peromyscus maniculatus and P. crinitus. Predators include raptorial birds, snakes, and predatory mammals. Cactus mice are host to at least 1 species of flea (Beck and Allred 1966).
Sources & References
California Department of Fish and Game, 1999.
California's Wildlife, Sacramento, CA.
Written by: P. Brylski, reviewed by: H. Shellhammer, edited by: R. Duke
Beatley, J. C. 1976b. Rainfall and fluctuating plant populations in relation to distributions and numbers of desert rodents in southern Nevada. Oecologia (Berlin) 24:21-42. Beck, D. E., and D. M. Allred. 1966. Siphonaptera (fleas) of the Nevada test site. Brigham Young Univ. Sci. Bull. Biol. Ser. No. 7. 27pp. Bradley, W. G., and R. A. Mauer. 1973. Rodents of a creosote-bush community in southern Nevada. Southwest. Nat. 17:333-344. Chew, R. M., and A. E. Chew. 1970. Energy relationships of the mammals of a desert shrub (Larrea tridentata) community. Ecol. Mongr. 40:1-21. Deacon, J. E., W. G. Bradley, and K. M. Larsen. 1964. Ecological distribution of the mammals of Clark Canyon, Charleston Mountains, Nevada. J. Mammal. 45:397-409. Grinnell, J. 1937. Mammals of Death Valley. Proc. Calif. Acad. Sci. 23:115-169. Lindeborg, R. G. 1952. Water requirements of certain rodents from xeric and mesic habitats. Contrib. Lab. Vertebr. Biol. Univ. Mich. No. 58. 32pp. MacMillen, R. E. 1964. Population ecology, water relations and social behavior of a southern California semidesert rodent fauna. Univ. Calif. Publ. Zool. 71:1-59. McCabe, T. T., and B. D. Blanchard. 1950. Three species of Peromyscus. Rood Assoc., Santa Barbara, Ca. 136pp. Meserve, P. L. 1976a. Habitat and resource utilization by rodents of a California coastal sage scrub community. J. Anim. Ecol. 45:647-666. Meserve, P. L. 1976b. Food relationships of a rodent fauna in a California coastal sage scrub community. J. Mammal. 57:300-319. Meserve, P. L. 1977. Three-dimensional home ranges of cricetid rodents. J. Mammal. 58:549-558. Miller, A. H., and R. C. Stebbins. 1964. The lives of desert animals in Joshua Tree National Monument. Univ. California Press, Berkeley. 452pp. Owings, D. H., and R. B. Lockard. 1971. Different nocturnal activity patterns of Peromyscus californicus and Peromyscus eremicus in lunar lighting. Psychonomic Sci. 22:63-64. Reichman, O. J., and K. M. Van de Graaff. 1973. Seasonal activity and reproductive patterns of five species of Sonoran Desert rodents. Am. Midl. Nat. 90:118-126. Rood, J. P. 1966. Observations on the reproduction of Peromyscus in captivity. Am. Midl. Nat. 76:496-503. Svihla, A. 1932. A comparative life history study of the mice of the genus Peromyscus. Univ. Mich. Mus. Zool., Misc. Publ. No. 24. 39pp. Veal, R., and W. Caire. 1979. Peromyscus eremicus. Mammal. Species No. 118. 6pp.
California Animal Facts | California's Wildlife